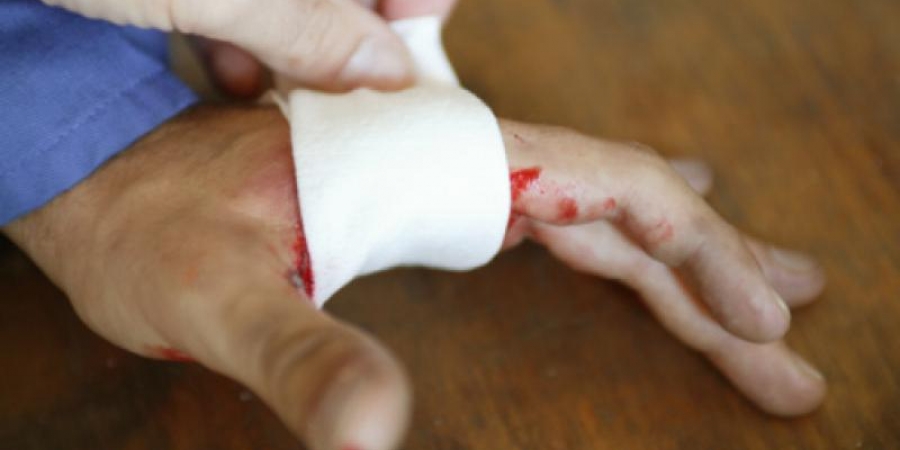
The fingertip is the part of the hand that is used to perform all the functions of the hand and is most exposed to external factors. At the fingertip there is a very nerve end that collects sensory impulses. It forms a protective layer against external trauma on the upper side of the fingertip. Functional and sensory data collection functions of the fingertip are extremely difficult to restore after trauma. The fingertip is most susceptible to crush injuries. Cutting tool, jamming, impact etc. injuries are common. Finger tip ruptures are the most common part of finger ruptures. Learning the type of trauma plays an important role in determining the treatment option. Circulatory and sensory examination is absolutely necessary. There may be injuries that may develop under the fingernail of the fingertip. Finger tip movements should be evaluated. The beams used to bend and lift the finger adhering to the last knuckle of the fingers may be disengaged from the attachment points during trauma. Radiological examination should be performed. In unexpected situations, bone fractures and small fractures may be detected.
Fingertip injuries are the most common areas of the hand due to the most common problem after the treatment. Restoring the support structure of the fingertip consisting of bone and nail; providing the pulp structure with certain softness and fullness; it is also the most extreme region that provides sensation and it is important to repair nerve structures in order to prevent any trauma due to the absence of sensation in the ongoing life.